Matthew Bennett

I am a data scientist working on time series forecasting (using R and Python 3) at the London Ambulance Service NHS Trust. I earned my PhD in cognitive neuroscience at the University of Glasgow working with fmri data and neural networks. I favour linux machines, and working in the terminal with Vim as my editor of choice.
Full Code
Below is all the code that we have written to date.
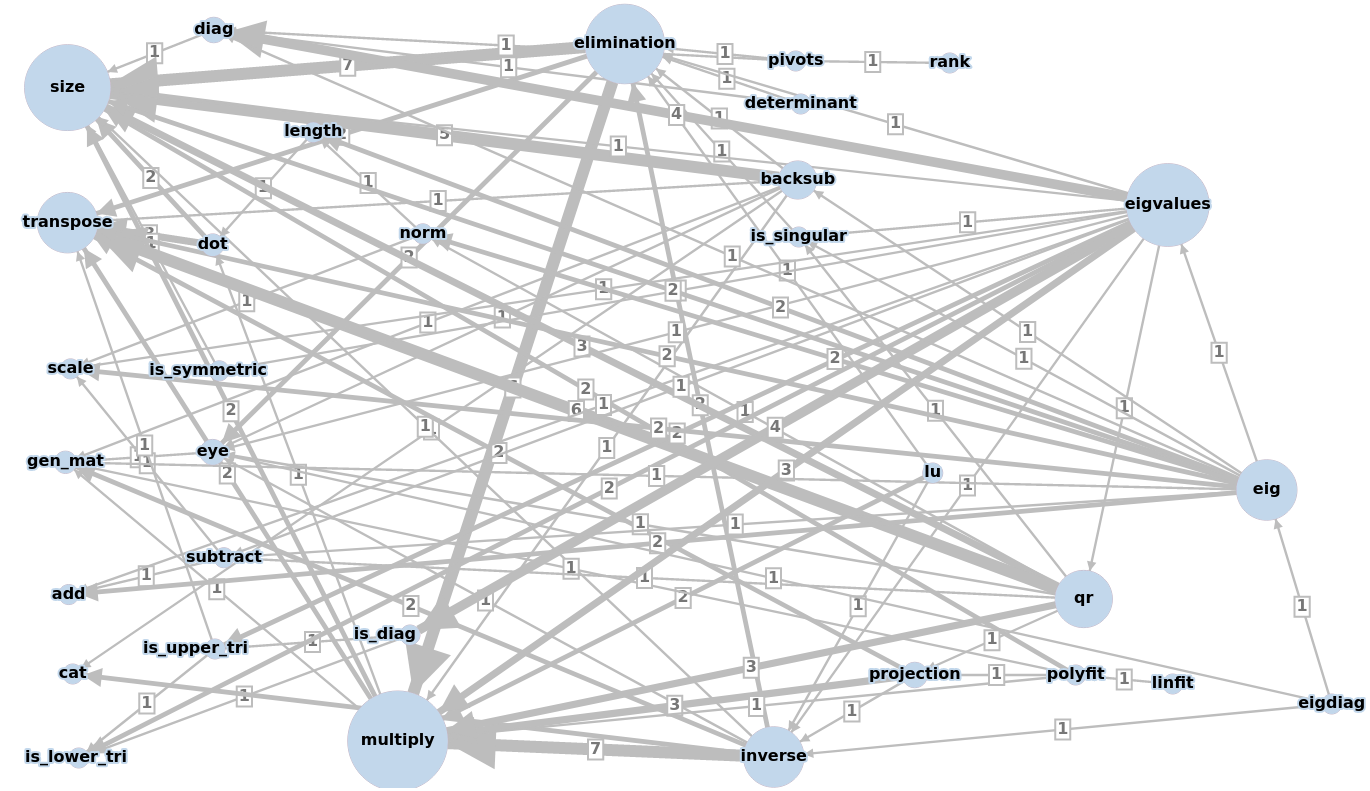
The dependencies among the methods are depicted by a weighted graph:
back to project main page
back to home
# Known bugs:
from copy import deepcopy as dc
from math import sqrt
def gen_mat(size, values=[0], kind='full'):
if type(size) is int:
size = [size, size]
if len(values) == 1:
values = [values[0] for val in range(max(size))]
elif len(values) < max(size):
values += [0 for val in range(max(size)-len(values))]
generated_mat = []
for i in range(size[0]):
row = []
for j in range(size[1]):
if (kind == 'diag' and j!=i) or (kind == 'upper' and j<=i) or (kind == 'lower' and j>=i):
row.append(0)
elif kind == 'diag':
row.append(values[j])
elif j>=i:
row.append(values[j-i])
elif j<i:
row.append(values[i-j])
generated_mat.append(row)
return Mat(generated_mat)
def eye(size):
return gen_mat(size, values=[1], kind='diag')
def cat(A, B, axis=0):
if axis == 0:
concatenated = Mat(A.data + B.data)
elif axis == 1:
concatenated = Mat([rows[0]+rows[1] for rows in zip(A.data, B.data)])
return concatenated
def print_mat(A, round_dp=99):
for row in A.data:
rounded = [round(j,round_dp) for j in row]
print(rounded)
print()
def vandermonde(n_rows, order=1):
A = gen_mat([n_rows, 1])
for i in range(n_rows):
orders = []
for exponent in range(order+1):
orders.append(i**exponent)
A.data[i] = orders
return A
class Mat:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
def transpose(self):
transposed = []
for i, row in enumerate(self.data):
for j, col in enumerate(row):
# first time through, make new row for each old column
if i == 0:
transposed.append([col])
else:
# append to newly created rows
transposed[j].append(col)
return Mat(transposed)
def ind(self, i=None, j=None):
if isinstance(i, int) and not isinstance(j, int):
return Mat([self.data[i]])
elif isinstance(j, int) and not isinstance(i, int):
return Mat([self.tr().data[j]]).tr()
elif isinstance(i, int) and isinstance(j, int):
return self.data[i][j]
def size(self, axis=2):
if axis == 0:
return len(self.data)
elif axis == 1:
return len(self.data[0])
elif axis == 2:
return [len(self.data), len(self.data[0])]
def make_scalar(self):
if max(self.size()) == 1:
return self.ind(0,0)
def is_square(self):
return self.size(0) == self.size(1)
def is_wide(self):
return self.size(0) < self.size(1)
def is_tall(self):
return self.size(0) > self.size(1)
def is_lower_tri(self):
for i, row in enumerate(self.data):
for col in range(i+1,len(row)):
if row[col] != 0:
return False
else:
return True
def is_upper_tri(self):
return self.tr().is_lower_tri()
def is_diag(self):
if self.is_lower_tri() and self.is_upper_tri():
return True
else:
return False
def is_symmetric(self):
for i in range(self.size(0)):
for j in range(i+1, self.size(0)):
if self.ind(i,j) != self.ind(i,j):
return False
else:
return True
def tile(self, axes=[1,1]):
B = dc(self)
for j in range(axes[1]-1):
self = cat(self, B, axis=1)
B = dc(self)
for i in range(axes[0]-1):
self = cat(self, B, axis=0)
return self
def function_elwise(self, function, B=None):
C = gen_mat(self.size())
for i in range(self.size(0)):
for j in range(self.size(1)):
if B:
C.data[i][j] = function(self.ind(i,j), B.ind(i,j))
else:
C.data[i][j] = function(self.ind(i,j))
return C
def function_choice(self, B, functions):
if isinstance(B, Mat) == False:
return self.function_elwise(functions[0])
return self.function_elwise(functions[1], B)
def add(self, B):
return self.function_choice(B, [lambda x: x+B, lambda x, y: x+y])
def subtract(self, B):
return self.function_choice(B, [lambda x: x-B, lambda x, y: x-y])
def multiply_elwise(self, B):
return self.function_choice(B, [lambda x: x*B, lambda x, y: x*y])
def div_elwise(self, B):
return self.function_choice(B, [lambda x: x/B, lambda x, y: x/y])
def dot(self, new_mat):
# make both vectors rows with transpose
if self.size(0) != 1:
self = self.tr()
if new_mat.size(0) != 1:
new_mat = new_mat.tr()
dot_prod = []
for cols in zip(self.data[0], new_mat.data[0]):
dot_prod.append(cols[0]*cols[1])
dot_prod = sum(dot_prod)
return dot_prod
def length(self):
return sqrt(self.dot(self))
def norm(self):
if self.length() != 0:
self = self.div_elwise(self.length())
return self
def multiply(self, new_mat):
# preallocate empty matrix
multiplied = gen_mat([self.size(0), new_mat.size(1)])
# transpose one matrix, take a bunch of dot products
new_mat = new_mat.tr()
for i, row in enumerate(self.data):
tmp_row = Mat([row])
for j, col in enumerate(new_mat.data):
# enter the dot product into our final matrix
multiplied.data[i][j] = tmp_row.dot(Mat([col]))
return multiplied
def diag(self):
diag_vals = []
for idx in range(min(self.size())):
diag_vals.append(self.ind(idx,idx))
return diag_vals
def elimination(self):
# should do some row exchanges for numerical stability...
# we assume the matrix is invertible
singular = False
# size of elimination and perumtation matrices
mat_size = [self.size(0)]*2
# create identity matrix which we'll turn into an E matrix
E = eye(mat_size)
# create a permutation matrix for row exchanges
P = eye(mat_size)
U = dc(self)
pivot_count = 0
row_exchange_count = 0
for idx in range(U.size(0)-1):
for sub_row in range(idx+1, U.size(0)):
# create elimination mat
nextE = eye(mat_size)
nextP = eye(mat_size)
# handle a zero in the pivot position
if U.data[idx][pivot_count] == 0:
row_exchange_count += 1
# look for a non-zero value to use as the pivot
options = [row[pivot_count] for row in U.data[sub_row:]]
exchange = sub_row + options.index(max(options, key=abs))
# build and apply a purmutation matrix
nextP.data[idx][pivot_count] = 0
nextP.data[idx][exchange] = 1
nextP.data[exchange][exchange] = 0
nextP.data[exchange][pivot_count] = 1
U = nextP.multiply(U)
P = nextP.multiply(P)
# check if the permutation avoided a zero in the pivot position
if U.data[idx][idx] == 0:
singular = True
# undo the row exchanges that failed
row_exchange_count -= 1
U = nextP.tr().multiply(U)
P = nextP.tr().multiply(P)
# move on to the next column
break
# determine how much to subtract to create a zero
ratio = U.data[sub_row][pivot_count]/U.data[idx][pivot_count]
# create the elimination matrix for this step
nextE.data[sub_row][idx] = -ratio
# apply the elimination step to U
U = nextE.multiply(U)
# update the overall E
E = nextE.multiply(E)
pivot_count += 1
# If self was a 1x1 matrix, the above loops didn't happen. Take the
# reciprocal of the number:
if U.size(0) == 1 and U.size(1) == 2:
if U.ind(0,0) != 0:
U.data[0] = [1/U.ind(0,0), 1]
i = -1
# check if the matrix is square
if U.size(1) == U.size(0):
# check if the permutation avoided a zero in the pivot position
if U.data[idx+1][idx+1] == 0:
singular = True
return P, E, self, U, singular, row_exchange_count
def backsub(self, b):
augmented = cat(self, b, axis=1)
_, _, _, U, _, _ = augmented.elimination()
coeff = []
for idx in range(-1, -(U.size(0)+1), -1):
if idx < -1:
E = eye([U.size(0)+1, U.size(1)])
E.data[idx][U.size(1)-1] = -1*(coeff[-1])
U = U.multiply(E)
row = U.data[idx]
# check solution possibilities
if row[idx-1] == 0 and row[-1] != 0:
print('No solution!')
return None
elif row[idx-1] == 0 and row[-1] == 0:
print('Infinite solutions!')
coeff.append(1)
else:
coeff.append(row[-1]/row[idx-1])
coeffs = list(reversed(coeff))
return Mat([coeffs]).tr()
def pivots(self):
_, _, _, U, _, _ = self.elimination()
# extract the first non-zero from each row - track the column number
U = U.tr()
pivots = {}
found = []
for j, col in enumerate(U.data):
piv_pos = sum(list(map(bool, col)))
if piv_pos not in found:
found.append(piv_pos)
pivots[j] = col[piv_pos-1]
return pivots
def rank(self):
return len(self.pivots())
def is_singular(self):
_, _, _, _, singular, _ = self.elimination()
return singular
def determinant(self):
# find U
_, _, _, U, _, row_exchange_count = self.elimination()
# muliply the pivots
det = 1
diag_vals = U.diag()
for val in diag_vals:
det *= val
# if an odd number of row exchanges, multiply determinant by minus one
if row_exchange_count % 2:
det *= -1
return det
def pivot_sign_code(self):
'''Returns number between 0 and 7 according to signs of pivots. We do
this by constructing a 3-bit binary number, where each bit represents
the presence/absence of negative, zero, or positive pivots, and then
converting from binary to a base 10 integer.'''
pivot_info = self.pivots().items()
neg = int(any(piv[1] < 0 for piv in pivot_info))
semi = int(len(pivot_info) < self.size(1))
pos = int(any(piv[1] > 0 for piv in pivot_info))
return int(str(neg) + str(semi) + str(pos), 2)
def is_negdef(self):
return self.pivot_sign_code() == 4
def is_negsemidef(self):
return self.pivot_sign_code() == 6
def is_possemidef(self):
return self.pivot_sign_code() == 3
def is_posdef(self):
return self.pivot_sign_code() == 1
def inverse(self):
mat_size = self.size()
# create [A I]
I = eye(mat_size)
augmented = cat(self, I, axis=1)
# perform elimination to get to [U ~inv]
_, _, _, U, singular, _ = augmented.elimination()
if singular:
print('Matrix is singular!')
return None
# seperate augmented into U and ~inv
tmp_fU = Mat([Urow[0:mat_size[1]] for Urow in U.data])
tmp_inv = Mat([Urow[mat_size[1]:] for Urow in U.data])
# create anti-diag I
antiI = gen_mat(mat_size)
for i, j in enumerate(reversed(range(mat_size[1]))):
antiI.data[i][j] = 1
# multiply U and ~inv on both sides by anti-diag I
fU = antiI.multiply(tmp_fU).multiply(antiI)
f_tmp_inv = antiI.multiply(tmp_inv).multiply(antiI)
# put fU back into [fU f~inv]
augmented = cat(fU, f_tmp_inv, axis=1)
# perform elimination again to get to [cI cA^-1]
_, _, _, U, _, _ = augmented.elimination()
# divide each row by c to get [I A^-1]
div = gen_mat(mat_size)
for idx in range(mat_size[0]):
div.data[idx][idx] = 1/U.ind(idx,idx)
inv = div.multiply(U)
# flip back
inv = antiI.multiply(inv)
for idx in range(mat_size[1]):
inv.data[idx] = inv.data[idx][mat_size[1]:]
inv = inv.multiply(antiI)
return inv
def lu(self):
P, E, A, U, _, _ = self.elimination()
E = P.multiply(E)
L = P.multiply(E.inverse())
return A, P, L, U
def projection(self):
# P = A((A'A)^-1)A'
AtA_inv = (self.tr().multiply(self)).inverse()
for_x = AtA_inv.multiply(self.tr())
Projection = self.multiply(for_x)
return Projection, for_x
def project_onto_A(self, A):
_, for_x = A.projection()
projected = for_x.multiply(self)
return projected
def polyfit(self, order=1):
V = vandermonde(self.size(0), order=order)
# fit model to b
return self.project_onto_A(V)
def linfit(self):
return self.polyfit()
def qr(self):
if self.is_singular():
print('Matrix is singular!')
return self, None, None
A = self.tr()
Q = dc(A)
I = eye(A.size())
# projection orthogonal to column
for col in range(Q.size(0)-1):
Col = dc(Mat([Q.data[col]]))
P, _ = Col.tr().projection()
P = I.subtract(P)
# project and put into matrix Q
for col2 in range(col+1, Q.size(0)):
Col = dc(Mat([Q.data[col2]]))
q = P.multiply(Col.tr()).tr()
Q.data[col2] = q.data[0]
# normalise to unit length
for x, q in enumerate(Q.data):
q = Mat([q])
q = q.norm()
Q.data[x] = q.data[0]
A = A.tr()
R = Q.multiply(A)
Q = Q.tr()
A = Q.multiply(R)
return A, Q, R
def eigvalues(self, epsilon = 0.0001, max_its=100):
if not (self.is_symmetric() or self.is_lower_tri() or self.is_upper_tri()):
print('Matrix is not symmetric or triangular and may therefore have complex eigenvalues which this method cannot handle. Interpret results with care!')
if self.is_upper_tri() or self.is_lower_tri():
return Mat([self.diag()])
if self.is_singular():
print('Matrix is singular!')
return None
old_eig = 0
final_eigs = []
for its in range(max_its):
# obtain off diagonal zeros
_, E, _, _, _, _ = self.elimination()
Einv = E.inverse()
A = E.multiply(self).multiply(Einv)
# shift A by -cI, where c is last diag
shift = eye(A.size()).multiply_elwise(old_eig)
# QR factorisation
A = A.subtract(shift)
_, Q, R = A.qr()
A = R.multiply(Q)
A = A.add(shift)
current_eig = A.diag()[-1]
diff = old_eig - current_eig
old_eig = current_eig
if abs(diff) < epsilon:
if min(A.size()) == 2:
final_eigs += A.diag()
return Mat([final_eigs])
else:
final_eigs.append(current_eig)
A = A.data[:-1]
A = [row[:-1] for row in A]
A = Mat(A)
old_eig = A.diag()[-1]
else:
print('Did not converge!')
return None
def eig(self, epsilon=0.0001, max_its=100):
if self.is_singular():
print('Matrix is singular!')
return None, None
evals = self.eigvalues()
evects = []
for evalue in evals.data[0]:
# ensure we don't destroy the diagonal completely
if evalue in self.diag():
evalue -= 1e-12
A_shifted = self.subtract(eye(self.size()).multiply_elwise(evalue))
# A_shifted_inv = A_shifted.inverse()
b = gen_mat([self.size(0),1], values=[1])
b = b.norm()
for its in range(max_its):
old_b = dc(b)
b = A_shifted.backsub(b)
# b = A_shifted_inv.multiply(b)
b = b.norm()
diff1 = b.subtract(old_b)
diff2 = b.subtract(old_b.multiply_elwise(-1))
if diff2.length() or diff2.length() < epsilon:
evects.append(b.tr().data[0])
break
evects = Mat(evects).tr()
return evects, evals
def eigdiag(self):
evects, evals = self.eig()
eigval_mat = gen_mat(self.size(), values=evals.data[0], kind='diag')
if self.is_symmetric():
evectsinv = evects.tr()
else:
evectsinv = evects.inverse()
return evects, eigval_mat, evectsinvback to project main page
back to home